Vitamin E is an essential, fat-soluble nutrient that is a potent antioxidant, contributing significantly to our overall health. Among its eight forms, alpha-tocopherol is the most beneficial for human dietary needs. You can find this vital nutrient in various foods, and it’s also added to some food items to enhance their nutritional value.1
What Is Vitamin E?
Vitamin E, also referred to as alpha-tocopherol, is a fat-soluble vitamin that acts as a potent antioxidant. It’s a vital nutrient for your body and needs to be included in your diet. Vitamin E has several important roles in the body, such as:
- Protecting Cells: It safeguards your cells from free radicals, which are molecules generated when your body metabolizes food or when it’s exposed to harmful environmental elements like tobacco smoke and radiation.2
- Immune System Support: Vitamin E aids your immune system and ensures its proper functioning.
- Health Maintenance: Vitamin E contributes to the health of your blood, brain, and skin.
- Vision and Reproduction: It’s also crucial for vision and reproduction.
Vitamin E can be obtained from various foods like canola oil, olive oil, margarine, almonds, peanuts, meats, dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals, as well as from dietary supplements.
The Benefits Of Vitamin E
Vitamin E offers a range of health benefits beyond those previously discussed. Here are some more:

- Cataract Prevention: Vitamin E might help in preventing the development of cataracts.
- Cognitive Health: It could enhance brain health and cognitive functions.
- Osteoarthritis Management: Vitamin E might be beneficial in managing osteoarthritis.
- Blood Clot Prevention: It could help in preventing blood clots.
- Delaying Premature Graying: Vitamin E might delay the onset of premature graying.
- Hand and Nail Care: It can nourish your hands and nails.
- Energy Boost: Vitamin E can help energize your body.
- Cancer Prevention: As an antioxidant, vitamin E aids in cancer prevention.3
- Stroke Prevention: It might help in preventing strokes.
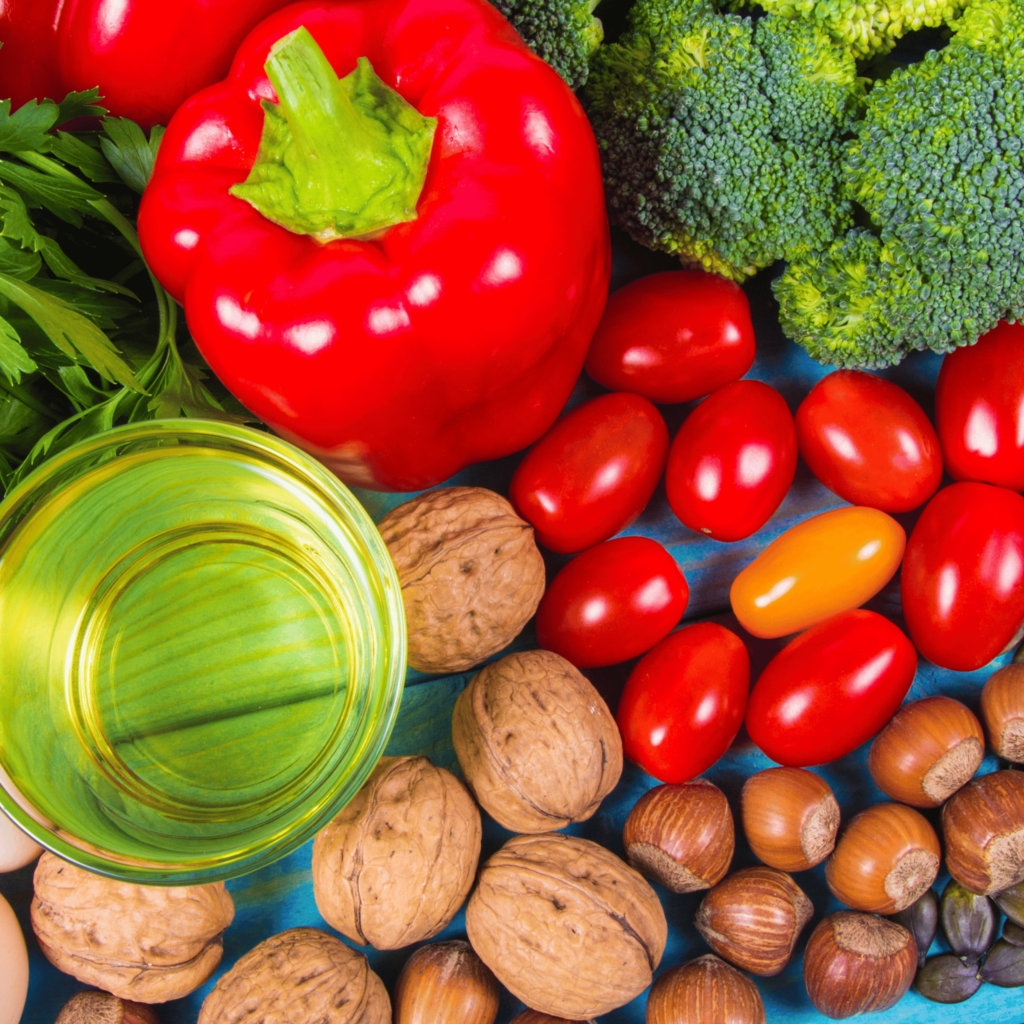
Sources Of Vitamin E
Vitamin E is abundant in various foods, so deficiency is uncommon unless there’s an issue with nutrient absorption. Here are some foods rich in Vitamin E:
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, peanuts, and hazelnuts are loaded with Vitamin E.
- Vegetable Oils: Wheat germ oil, sunflower oil, safflower oil, and olive oil are great sources.4
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Spinach, broccoli, turnip greens, and beet greens have high Vitamin E content.
- Fruits: Kiwi and mangoes are good sources.
- Seafood: Trout and abalone are rich in Vitamin E.

Supplements
Here are some Vitamin E supplements you might want to look into:
- Nordic Naturals Vitamin E Complex: A top-rated overall vitamin E supplement5
- Pure Encapsulations Vitamin E: A Leading Softgel Vitamin E Supplement
- Nature Made Natural Vitamin E: Runner-up for Best soft gel Vitamin E supplement.
- Garden of Life Vitamin Code Raw Vitamin E: Top vegan-friendly Vitamin E supplement.
- CVS Health Vitamin E: Best for high-dose Vitamin E supplement.
- Nature Made Synthetic Vitamin E: Highest-rated Vitamin E supplement.
- Kirkland Signature Vitamin E: Most budget-friendly Vitamin E supplements.
- OLLY The Perfect Women’s Multi: Best multivitamin with Vitamin E for women.
- Nature Made Multi for Him: The best multivitamin with Vitamin E for men.

Vitamin E-Rich Recipes
Here are some recipes that are rich in Vitamin E:
- Vitamin C Power Smoothie: This refreshing smoothie is filled with chunks of fresh pineapple, medium-sized naval oranges, a large mango, ginger, a ripe banana, and ice.
- Nutrient-Dense Smoothie: This plant-based recipe features a grapefruit, a carrot, half an apple, half an orange, a slice of ginger, and water.
- Avocado Salad: This salad, inspired by Indian cuisine, is a powerhouse of antioxidants, including vitamin E.6
- Swiss Chard and Kohlrabi with Lemon Sauce: A tasty and nutritious dish that’s rich in Vitamin E
- Eggs Anytime: A flexible recipe that can be savored at any time of the day
- Crunchy Broccoli: A delightful way to enjoy this vegetable that’s high in Vitamin E
Symptoms Of Vitamin E Deficiency
A lack of Vitamin E is uncommon unless there’s a specific health issue. However, certain signs might indicate a deficiency. These include:
- Challenges with walking or maintaining balance
- Muscle discomfort or frailty
- Problems with vision
- Feeling unwell in general
These symptoms suggest potential harm to the central and peripheral nervous systems. If you notice any of these signs, it’s advised to consult a medical professional.
Vitamin E Deficiency Risk Factors
Vitamin E deficiency is uncommon and typically results from insufficient dietary intake or a condition that impairs fat absorption. Certain medical conditions can hinder fat absorption, which in turn reduces Vitamin E absorption and heightens the risk of Vitamin E deficiency. These conditions include:
- Pancreatitis
- Liver disorders
- Gallbladder abnormalities
- Cystic Fibrosis

Safety And Side Effects
When consumed in suitable amounts, Vitamin E is generally considered safe for oral intake. However, high doses can lead to certain side effects7, such as:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Skin rash
- Gonadal dysfunction
- Increased creatine concentration in urine
Long-term consumption of large doses (exceeding 1,000 mg daily) may result in headaches, nausea, blurred vision, and thyroid gland disturbances. It’s recommended to avoid high-dose intake of Vitamin E (more than 400 mg per day).
Recommended Amounts
The daily recommended intake of Vitamin E for adults is 15 milligrams. For supplements, whether natural or synthetic, the upper limit for adults is set at 1,000 mg/day. This equates to 1,500 IU/day for natural Vitamin E supplements and 1,100 IU/day for synthetic ones.8 The upper limits for children are lower compared to adults. It’s always important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Toxicity
Vitamin E toxicity, also referred to as an overdose of Vitamin E, happens when an excess amount of Vitamin E accumulates in your body, leading to health issues. Vitamin E, a fat-soluble vitamin, acts as an antioxidant.9 Consuming it in large quantities can result in it accumulating in your body fat, which can cause problems.
To avoid Vitamin E toxicity, ensure that your daily intake of Vitamin E from both supplements and food does not exceed 1,000 mg. If you think you might have Vitamin E toxicity, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical advice. The usual treatment for Vitamin E toxicity involves either discontinuing the vitamin or reducing the intake to less than the upper limit of 1000 mg per day.

Final Words
Vitamin E is a vital nutrient that plays a significant role in many bodily functions. It acts as a powerful antioxidant, supports the immune system, and contributes to eye, brain, and skin health. It’s found in various foods like nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, green leafy vegetables, and fruits. While Vitamin E deficiency is rare, it can lead to symptoms like difficulty with walking or coordination, muscle pain or weakness, visual disturbances, and general unwellness.
On the other hand, Vitamin E toxicity can occur if an excessive amount of Vitamin E builds up in the body. Therefore, it’s important to maintain a balanced intake of Vitamin E through diet or supplements as advised by a healthcare professional.
FAQs
Sources
- Kubala, Jillian. “All about Vitamin E: Benefits, RDA, and More.” Healthline, 19 Jan. 2022, www.healthline.com/health/all-about-vitamin-e. Accessed 24 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- Mayo Clinic. “Vitamin E.” Mayo Clinic, 2017, www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-vitamin-e/art-20364144. Accessed 24 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- “What You Need to Know about Vitamin E Supplements.” Verywell Fit, www.verywellfit.com/vitamin-e-supplements-what-you-need-to-know-90042. Accessed 24 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- Arnarson, Atli. “20 Foods That Are High in Vitamin E.” Healthline, 24 May 2017, www.healthline.com/nutrition/foods-high-in-vitamin-e. Accessed 24 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- “10 Best Vitamin E Supplements in the Philippines 2023 | Buying Guide Reviewed by Pharmacist.” Mybest, ph.my-best.com/16358. Accessed 24 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- “What Is Vitamin E?” BBC Good Food, www.bbcgoodfood.com/howto/guide/what-vitamin-e. Accessed 24 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- “Vitamins A, c and E.” Versus Arthritis, www.versusarthritis.org/about-arthritis/complementary-and-alternative-treatments/types-of-complementary-treatments/vitamins-a-c-and-e/. Accessed 24 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- National Institutes of Health. “Office of Dietary Supplements – Vitamin E.” Nih.gov, 22 Mar. 2021, ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminE-Consumer/. Accessed 24 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- “Vitamin E Overdose: Symptoms, Side Effects, and Treatment.” Healthline, 5 May 2020, www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-e-overdose#treatment-prevention. Accessed 24 Oct. 2023. ↩︎