The immune system is a complex structure made up of various cells, organs, proteins, and tissues. Its main function is to safeguard the body from harmful intruders such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Components Of The Immune System
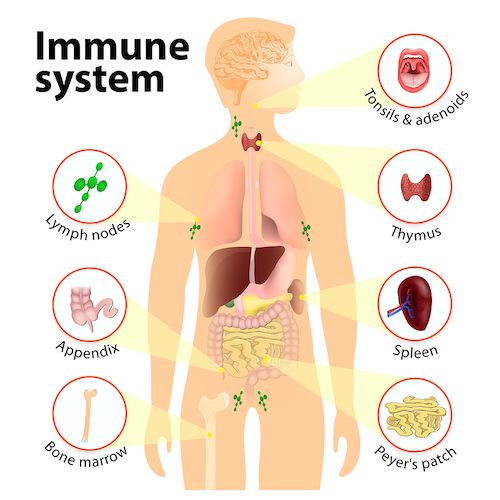
The immune system is made up of various elements, including white blood cells or leukocytes, the spleen, bone marrow, the lymphatic system, the thymus, tonsils, adenoids, and the appendix.1
White blood cells circulate through the blood and lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic system is a network similar to blood vessels that transport a fluid called lymph instead of blood. This lymph fluid carries cells related to immunity to the necessary areas.
White blood cells are stored in various locations, known as lymphoid organs. These include:
- The thymus: This is a gland located behind the breastbone where a type of white blood cell known as lymphocytes mature.
- The spleen: This organ is located in the upper left part of the abdomen and is where immune cells congregate and function.
- Bone marrow: This is the soft tissue found in the center of bones that produces both red and white blood cells.
- Lymph nodes: These are small, bean-shaped glands located throughout the body. They are connected via lymphatic vessels. Immune cells gather in lymph nodes and respond when antigens are detected.
Types Of White Blood Cells
White blood cells, or leukocytes, are important components of the immune system that safeguard the body from infections. There are various types of white blood cells, each with a unique role.
- Neutrophils: These cells constitute about half of the body’s white blood cells and are typically the first to respond to harmful invaders like bacteria or viruses.
- Lymphocytes: These exist in two forms: B cells and T cells. B lymphocytes (B cells) are involved in humoral immunity, the immune response involving antibodies. T lymphocytes (T cells) participate in cell-mediated immunity.
- Monocytes: These cells are part of our innate immune system and can attack foreign substances from birth.
- Eosinophils: These cells help combat bacteria and parasitic infections (such as worms). They are most known for their role in triggering allergy symptoms.
- Basophils: These cells play a significant role in asthma and are part of the body’s basic immune response to harmful organisms.
- Natural killer cells: These cells can kill cells infected with certain viruses or cancer cells.
- Macrophages: These large white blood cells exist in every body tissue and consume pathogens and damaged or dead cells.
- Dendritic cells: These serve as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems.
- Mast cells: These play an important role in the inflammatory process.
- Plasma cells: These white blood cells produce antibodies that fight diseases.
- Memory cells: These are long-lived lymphocytes that have previously encountered and responded to their cognate antigen.
- Regulatory T cells (Tregs): These suppress or downregulate the induction and proliferation of effector T cells.
- T helper cell (Th cell): These assist other white blood cells in immunologic processes, including maturation of B cells into plasma and memory B cells and activation of cytotoxic T cells and macrophages.
- Cytotoxic T cell (Tc cell): These destroy virus-infected cells and tumor cells and are implicated in transplant rejection.
- Natural killer T cells (NKT cells): These bridge the adaptive immune system with the innate immune system.
Types Of Immune System
- Innate Immune System: This is the immune system we are born with. It offers a pre-set response to a wide variety of situations and stimuli. It includes mechanisms such as phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides known as defensins, and the complement system.
- Adaptive Immune System: This immune system develops when our body is exposed to microbes or chemicals released by microbes. It provides a customized response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules previously encountered.
These two immune systems work in tandem to protect our bodies from infections and diseases.
How Does The Immune System Work?
When a pathogen enters the body, the immune system identifies it as an invader. This begins an immune response that typically involves four stages:
- Identification: The immune system recognizes the pathogen as a foreign entity.
- Activation: The white blood cells are stimulated to respond to the identified pathogen.
- Response: The immune system launches an attack to eliminate the pathogen.
- Memory: Certain white blood cells, known as memory cells, retain information about the pathogen for a faster response if it invades again in the future.
How To Boost the Immune System
Enhancing your immune system requires a few lifestyle modifications:
- Get Enough Sleep: Enough sleep is crucial for a robust immune system. Aim for 7 or more hours of sleep each night.
- Consume Whole Plant Foods: Whole plant foods like fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and legumes are packed with nutrients and antioxidants that can aid your body in combating harmful pathogens.
- Incorporate Healthy Fats: Healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil and salmon, can enhance your body’s immune response to pathogens by reducing inflammation.
- Regular Exercise: Consistent physical activity can strengthen your immune system and help prevent infections.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity can compromise your immune system, so keeping a healthy weight may enhance your immunity.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can weaken your immune system. If you smoke, quitting is the best thing you can do for your immune system.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: It’s important to drink alcohol moderately, if at all, as it can weaken the immune system.
- Prevent Infections: This includes frequent hand washing and thoroughly cooking meats.

Common Immune System Disorders
- Allergies: These happen when the immune system responds to substances in the environment that are typically harmless.
- Autoimmune diseases: These happen when the immune system erroneously attacks the body’s own cells.
Examples include:
- Type 1 diabetes: The immune system targets the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: This form of arthritis results in swelling and deformities of the joints.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): This is a long-term autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body.2
- Multiple sclerosis (MS): This is a potentially debilitating disease of the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
3. Immune deficiency diseases: These occur when the immune system is not functioning correctly.
Examples include:
- Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID): This is an example of an immune deficiency that is present at birth.
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS): HIV, which causes AIDS, is an acquired viral infection that destroys important white blood cells and weakens the immune system.
Weak Immune System
A weak immune system is a state where the body’s defense mechanism against infections and diseases is impaired or completely non-functional3. Various factors can lead to this condition, such as aging, certain cancers, malnutrition, viral hepatitis, specific medical treatments, and autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease.
Causes Of Weak Immune System
A weak immune system can be caused by a variety of factors:
- Age: Aging is the most prevalent cause of a compromised immune system.4
- Unhealthy lifestyle: Factors such as insufficient sleep, an inactive lifestyle, lack of sunlight, and a diet primarily composed of processed foods can contribute to a weakened immune system.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can instantly weaken immune defenses as it directly affects the bone marrow.
- Medications: Prolonged use of steroids and other immune-suppressing drugs (including Imuran, Plaquenil, and biologic agents) can impair the immune system.
- Immune system disorders: Any condition that hampers the normal functioning of the immune system falls under this category.
- Autoimmune diseases: These are a type of immune system disorder where the immune system erroneously identifies a part of the body as a potential infection source and attacks it.
Signs And Symptoms Of Weak Immune System
- Frequent Infections: Individuals with a weakened immune system are prone to getting infections more often than others, which might be more severe or difficult to treat.
- Cold Hands: If your blood vessels are inflamed, it could be challenging for your fingers, toes, ears, and nose to stay warm.
- Bathroom Problems: Persistent diarrhea lasting more than 2 to 4 weeks could suggest that your immune system is damaging the lining of your small intestine or digestive tract.5
- Dry Eyes: Many individuals with an autoimmune disorder experience dry eyes.
- Fatigue: Feeling extremely exhausted, similar to when you have the flu, could indicate that something is affecting your body’s defenses.
- Mild Fever: If you’re experiencing a higher temperature than usual, it could mean your immune system is starting to overwork. Headaches: Sometimes, headaches can be associated with the immune system.

Overactive Immune System
An overactive immune system is a condition where the immune system reacts too strongly to typically harmless substances in the environment. This overreaction can lead to disorders such as allergies, asthma, or eczema.6
Causes Of Overactive Immune System
- Genetics: Certain inherited genes may cause your immune system to react to substances in the environment that are typically harmless.
- Allergens: An allergic reaction is the most frequent instance of an overactive immune system. Allergens can include dust, mold, pollen, and certain foods.
- Autoimmune diseases: In these conditions, the immune system erroneously attacks healthy cells in the body. Rheumatoid arthritis and type 1 diabetes are examples of such diseases.
- Environmental factors: Specific environmental factors can also provoke an overactive immune response. This can include exposure to certain chemicals or toxins.
Signs And Symptoms Of Overactive Immune System
- Cold Hands: Inflammation of your blood vessels can make it difficult for your fingers, toes, ears, and nose to stay warm.7
- Bathroom Problems: Persistent diarrhea lasting more than 2 to 4 weeks could be an indication that your immune system is damaging the lining of your small intestine or digestive tract. Constipation could also be an issue.
- Dry Eyes: Many individuals with an autoimmune disorder experience dry eyes.
- Fatigue: Feeling extremely exhausted, similar to when you have the flu, could indicate that there’s something affecting your body’s defenses.
- Mild Fever: If you’re experiencing a higher temperature than usual, it could mean that your immune system is starting to overwork.
- Headaches: Sometimes, headaches can be associated with the immune system.
- Asthma: The reaction in your lungs can result in coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
- Eczema: An allergen can cause an itchy rash known as atopic dermatitis.
- Allergic rhinitis: Symptoms can include sneezing, a runny nose, and sniffling.
How To Prevent Overactive Immune System
- Relaxation: Lower your stress levels by listening to soothing music or practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or guided imagery.
- Healthy Diet: Your diet should include fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. Avoid adding salt, sugar, high-cholesterol foods, saturated fat, and trans fat to your diet.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for eight hours of sleep per day to rejuvenate your mind and body. This is particularly crucial for individuals with immune system issues. Enough rest helps in fighting stress and illness.
- Exercise: Begin a gentle exercise regimen such as yoga or tai chi. Rigorous exercise with an overactive immune system can quickly lead to fatigue and exacerbate your symptoms.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can impair your immune system and increase your susceptibility to diseases.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation.

Treatments For Immune System Disorders
- Self-care: This involves maintaining a nutritious, balanced diet and avoiding alcohol, drugs, and tobacco. Infection
- Management: Infections necessitate swift and aggressive treatment with antibiotics. Some individuals may require long-term antibiotics to prevent respiratory infections and lasting damage to the lungs and ears.
- Immunoglobulin Therapy: Immunoglobulin, which comprises antibody proteins necessary for the immune system to combat infections, can be administered either intravenously or via subcutaneous infusion.
- Stem Cell Transplantation: Stem cell transplantation provides a permanent solution for several types of life-threatening immunodeficiency.
- Over-the-counter Therapies: Over-the-counter (OTC) therapies do not require prescriptions and may be among the initial treatments your healthcare provider recommends for an autoimmune disease.
- Prescriptions: If you have severe symptoms or OTC therapies are ineffective, you may need to take prescription medications for autoimmune disorders.8
- Immunosuppressant Therapies: Immunosuppressive therapies can treat various types of autoimmune diseases. These medications suppress different parts of your immune system.
Keeping Your Immune System Healthy
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is beneficial for your immune system. This involves consuming a diet that is balanced and abundant in fruits and vegetables, engaging in regular physical activity, getting sufficient sleep, and managing stress effectively.

Final Words
The immune system is a remarkable defense network composed of cells, tissues, and organs that collaboratively shield our bodies from harmful intruders. It’s an unsung hero, tirelessly warding off common illnesses like colds and combating more severe diseases. However, it can encounter difficulties such as being underactive (immunodeficiency) or overactive (hypersensitivity). Comprehending its functions and maintaining its balance is essential for good health. Always remember a healthy lifestyle fosters a robust immune system! Stay knowledgeable and maintain your health.
FAQs
Sources
- Cleveland Clinic. “Immune System: Parts & Common Problems.” Cleveland Clinic, 23 Feb. 2020, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21196-immune-system. Accessed 30 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- “List of Autoimmune Diseases, with Symptoms and Treatments.” Www.medicalnewstoday.com, 30 June 2020, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/list-of-autoimmune-diseases. Accessed 30 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- Fletcher, Jenna. “Weak Immune System: Symptoms and What to Do.” Www.medicalnewstoday.com, 3 June 2020, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324930. Accessed 30 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- McKnight, Leah Campbell, Jason. “How to Tell If You Have a Weak Immune System.” Insider, www.insider.com/guides/health/what-causes-a-weak-immune-system. Accessed 30 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- Booth, Stephanie. “16 Symptoms of Immune System Problems.” WebMD, WebMD, 30 Oct. 2015, www.webmd.com/cold-and-flu/immune-system-disorders. Accessed 30 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- John Hopkins Medicine. “Disorders of the Immune System.” John Hopkins Medicine, 2019, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/disorders-of-the-immune-system. Accessed 30 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- Mayo Clinic. “Primary Immunodeficiency – Symptoms and Causes.” Mayo Clinic, 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/primary-immunodeficiency/symptoms-causes/syc-20376905. Accessed 30 Oct. 2023. ↩︎
- “How Autoimmune Diseases Are Treated.” Verywell Health, www.verywellhealth.com/how-autoimmune-diseases-are-treated-5093794. Accessed 30 Oct. 2023. ↩︎