Are you struggling with skin issues, heart health, or a restless mind? Instead of countless treatments, consider the powerful force of Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA). This omega-6 fatty acid goes beyond contemporary science, drawing from ancient remedies and offering remarkable benefits.
What is Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA)?
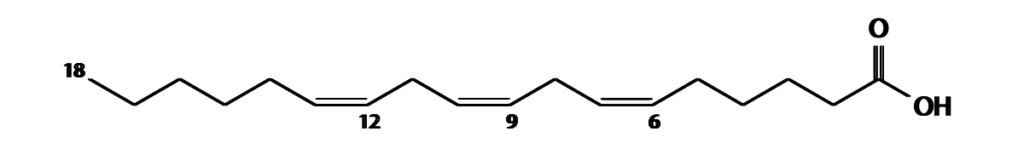
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) is an omega-6 fatty acid found in various plant-based oils such as evening primrose (EPO), borage oil, and black currant seed oil1. GLA, along with omega-3 fatty acids, plays a crucial role in brain function, normal growth and development, skin and hair growth, bone health, metabolism regulation, and maintaining the reproductive system.
The body converts linoleic acid (LA) to GLA and then to arachidonic acid (AA)2. Gamma-linolenic acid can also be obtained directly from plant-based oils.
A healthy diet should contain a balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. However, the typical American diet contains significantly more omega-6 fatty acids than omega-3 fatty acids, which may contribute to the high prevalence of inflammatory diseases in the American population.
Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA) is an essential omega-6 fatty acid found in plant oils such as borage, evening primrose, and black currant seed, known for its anti-inflammatory properties and benefits in brain function and skin health.
Food Sources
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) is a key omega-6 fatty acid essential for many bodily functions. Since our body can’t produce GLA independently, it’s vital to know where to find it in our diet.
- Borage Oil (18-26% GLA): From starflower seeds, borage oil is packed with Gamma-Linolenic Acid, boasting about 24% of its content.
- Spirulina: This blue-green algae, among the world’s most nutritious foods, is rich in GLA, making up to 40% of its total fatty acids.
- Evening Primrose Oil (7-10%): A medicinal oil from primrose seeds, it’s a long-standing source of GLA.
- Black Currant Seed Oil (15-20%): Extracted from black currant seeds, this oil is another GLA provider.
- Hemp Seed Oil (3%): Hemp oil offers GLA and other valuable fatty acids in various amounts.
These natural food sources offer a straightforward way to ensure our intake remains consistent, promoting overall balance in our body’s functions.
Understanding GLA’s Role in Our Body
Gamma-linolenic acid, or GLA for short, is a special fat that plays a big role in how our body deals with swelling and pain. Let’s take a closer look at what GLA does and why it’s important.
| Aspect of GLA | Details |
|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory properties | GLA helps reduce swelling, redness, and pain in the body. |
| Mechanism: Transformation of linoleic acid | Linoleic acid, an essential fatty acid, is converted into GLA. This GLA then turns into compounds like DGLA and PGE1, which are vital for health. PGE1 is particularly known for its anti-inflammatory properties. |
| Modulation of inflammation | GLA modulates inflammation, ensuring it doesn’t become chronic or excessive. It’s not about eliminating inflammation but about keeping it in check. |
| Implications for autoimmune conditions | GLA can help manage autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis by reducing pain and swelling. |
| Bioactive Metabolites | As the body processes GLA, it produces compounds like PGE1. These compounds have their own health benefits. |
| Dietary Importance | The conversion of linoleic acid to GLA can be inefficient due to factors like aging and stress. This underlines the need for direct GLA dietary sources. |
| Potential Side Effects | Excessive GLA might cause complications. It’s essential to understand the right amounts to consume. |
While Gamma-Linolenic Acid offers numerous health benefits, understanding its sources, mechanisms, and potential interactions is crucial.
Health Benefits of GLA
The ancient moniker of Gamma-Linolenic Acid as the “king’s cure-all” stems from its use in homeopathic remedies and folk cures3. Historically, it’s been championed for a plethora of conditions:

- Skin Conditions: Eczema and acne sufferers have reported relief from GLA, potentially due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Diabetic Complications: Nerve problems due to diabetes, termed diabetic neuropathy, and Diabetic nephropathy, a kidney condition, might benefit from GLA supplementation. However, while some studies suggest potential benefits, more rigorous research is imperative.
- Cardiovascular Health: High blood pressure (hypertension) might see modulation under GLA.
- Reproductive Health: From alleviating mastalgia (breast pain) and menopausal symptoms to providing relief of PMS symptoms, GLA shows diverse applications.
- Bone Health: Preliminary research indicates a potential role of GLA in combating osteoporosis.
- Mental Health: Some early evidence links GLA to relief in Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms.
- Cancer Therapy: The potential of GLA in breast cancer treatment is under exploration, specifically regarding its ability to increase lymphocytes, essential cells in the immune response.
Dosage Recommendations
Studies have often employed a Gamma-Linolenic Acid dosage range of 0.5 to 3 g per day4.
While there’s no standard GLA dosage due to the lack of official endorsement for specific ailments, various studies, and user experiences have led to certain commonly suggested dosages:
| Condition/Usage | Recommended GLA Dose (mg/day) |
|---|---|
| Weight Management | 890 mg |
| Diabetic Neuropathy | 360-480 mg |
| Immune & Inflammation Disorders | 1,400-2,800 mg |
| Dry Eye Conditions | 30-50 mg |
| Eczema (Adults) | 160-480 mg |
| Eczema (Children) | 80-320 mg |
| Cardiovascular Health | 240-560 mg |
However, the exact amount can vary based on individual conditions and should always be determined in consultation with a healthcare professional. Specific populations, such as pregnant women, are advised against using Gamma-Linolenic Acid unless under strict medical guidance.
Interactions
Like all bioactive compounds, Gamma-Linolenic Acid isn’t without its cautions. Some potential side effects, although usually mild, encompass acid reflux, diarrhea, itchiness, nausea, problems with concentration, stomach pain, and fatigue.
Notably, at dosages of 2.8 grams per day, Gamma-Linolenic Acid is possibly safe for most adults but might cause some digestive tract side effects.
Caution is advised when GLA is taken concomitantly with certain medications:
- Blood-Thinning Medications: As GLA might slow blood clotting, combining it with anticoagulant drugs could increase bleeding risks5.
- Ceftazidim and Chemotherapy for Cancer: Concurrent use might diminish the efficacy of these drugs.
- Cyclosporine: GLA might increase the side effects of this immunosuppressive drug.
- Phenothiazines: Used for schizophrenia, combining them with GLA might increase the risk of seizures.
Side Effects of Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA)
Like many medications and natural supplements, GLA can cause side effects in some individuals.
Common Side Effects
The most frequently observed side effects of GLA are usually mild and can include:
- Acid reflux
- Diarrhea
- Itchiness
- Nausea
- Problems with concentration or focus
- Stomach pain
- Tiredness or fatigue
Severe Side Effects
A study noted that GLA derived from evening primrose oil showed no significant severe side effects. However, like any supplement or medication, there’s always a risk of a severe allergic reaction.
Signs of a severe allergic reaction to GLA, or the plants it’s derived from, can include:
- Breathing difficulties
- Intense itchiness
- Rash
While omega-6 fatty acids like GLA can reduce inflammation, they might also promote inflammation in high doses or over prolonged periods. This could potentially lead to heart-related complications.

GLA Precautions
Allergic Histories
- Avoid GLA if you’ve previously had a severe allergy to it or its source plants.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Most individuals —including pregnant and breastfeeding individuals— consume omega-6 fatty acids in 5% to 10% of total calories through their diets. Evening primrose oil, a GLA source, may be suitable during these stages.
- High omega-6 fatty acid intake might pose fetal or infant risks. Borage seed oil, another GLA source, contains compounds that could harm the liver and respiratory system. Always consult before GLA supplementation during these periods.
Children
- Some GLA studies have involved children, but many product labels are adult-focused. Consult a pediatrician before administering GLA to children.
Senior Usage (65+ years)
- While seniors have been part of GLA studies, these were limited. Older adults, potentially more sensitive to medication reactions, should use GLA cautiously.
Heart-Related Conditions
- Extended or high-dose omega-6 fatty acid intake can impact cardiac health.^[2^] If you have heart conditions, monitor GLA use closely with a healthcare professional.
Always consult with a healthcare specialist for tailored advice.

Final Thoughts
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) benefits skin, heart, and mental health. Rooted in both tradition and research, its potential is significant. However, always consult healthcare professionals before integrating GLA into your regimen to ensure safety and efficacy.
FAQs
What are the benefits of GLA?
GLA has anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects, potentially benefiting various health concerns.
How is GLA used in skincare?
Gamma Linolenic Acid (GLA) is a skin-soothing agent used topically in skincare products to help calm and moisturize the skin.
Is GLA good for brain health?
Yes, GLA is essential for maintaining brain function and supporting skeletal health, reproductive health, and metabolism.
Which supplement contains the most GLA?
Borage oil is known to be one of the richest dietary sources of GLA, making it a popular choice for supplementation.
Who should consider taking GLA supplements?
GLA supplements may be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetic neuropathy, among others seeking its potential health benefits.
What is the best time of day to take GLA supplements?
Taking GLA supplements after meals is generally recommended to improve absorption and reduce the risk of stomach upset.
Can GLA help with acne?
It may help reduce acne due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
Are there any side effects associated with GLA supplementation?
Generally safe, but consult a healthcare professional before starting.
Can you get GLA from food sources?
Yes, plant oils like evening primrose and borage contain GLA.
Can GLA interact with medications or medical conditions?
Consult a healthcare provider if you’re on medication before taking GLA supplements.
Sources
- “Gamma Linolenic Acid.” RxList, RxList, 17 Sept. 2019, www.rxlist.com/gamma_linolenic_acid/supplements.htm. Accessed 20 Sept. 2023. ↩︎
- “Gamma-Linolenic Acid – an Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.” Sciencedirect.com, 2014, www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/gamma-linolenic-acid. Accessed 20 Sept. 2023. ↩︎
- “The Benefits of GLA.” Healthline, 20 Sept. 2023, www.healthline.com/health/gla-fit-for-a-king. Accessed 20 Sept. 2023. ↩︎
- https://www.facebook.com/Drugscom. “Gamma Linolenic Acid (GLA).” Drugs.com, Drugs.com, 2020, www.drugs.com/npc/gamma-linolenic-acid-gla.html. Accessed 20 Sept. 2023. ↩︎
- “Gamma-Linolenic Acid Information | Mount Sinai – New York.” Mount Sinai Health System, 20 Sept. 2023, www.mountsinai.org/health-library/supplement/gamma-linolenic-acid. Accessed 20 Sept. 2023. ↩︎