Hash oil, commonly referred to as concentrated cannabis, is a potent derivative of the Cannabis sativa plant. Its primary psychoactive component, THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol), is present in much higher concentrations than in typical marijuana products, making it a sought-after option for those looking for intensified effects.
Composition and Characteristics of Hash Oil
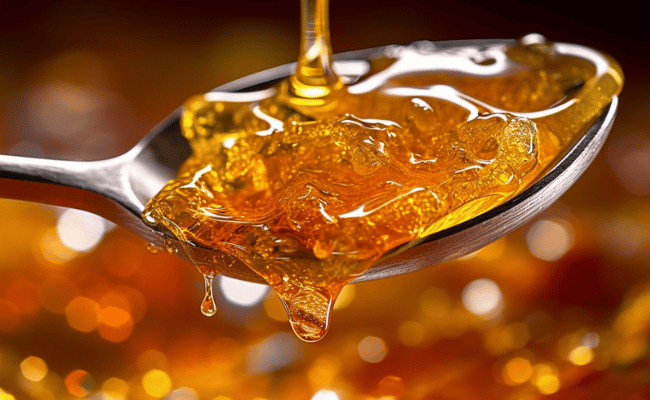
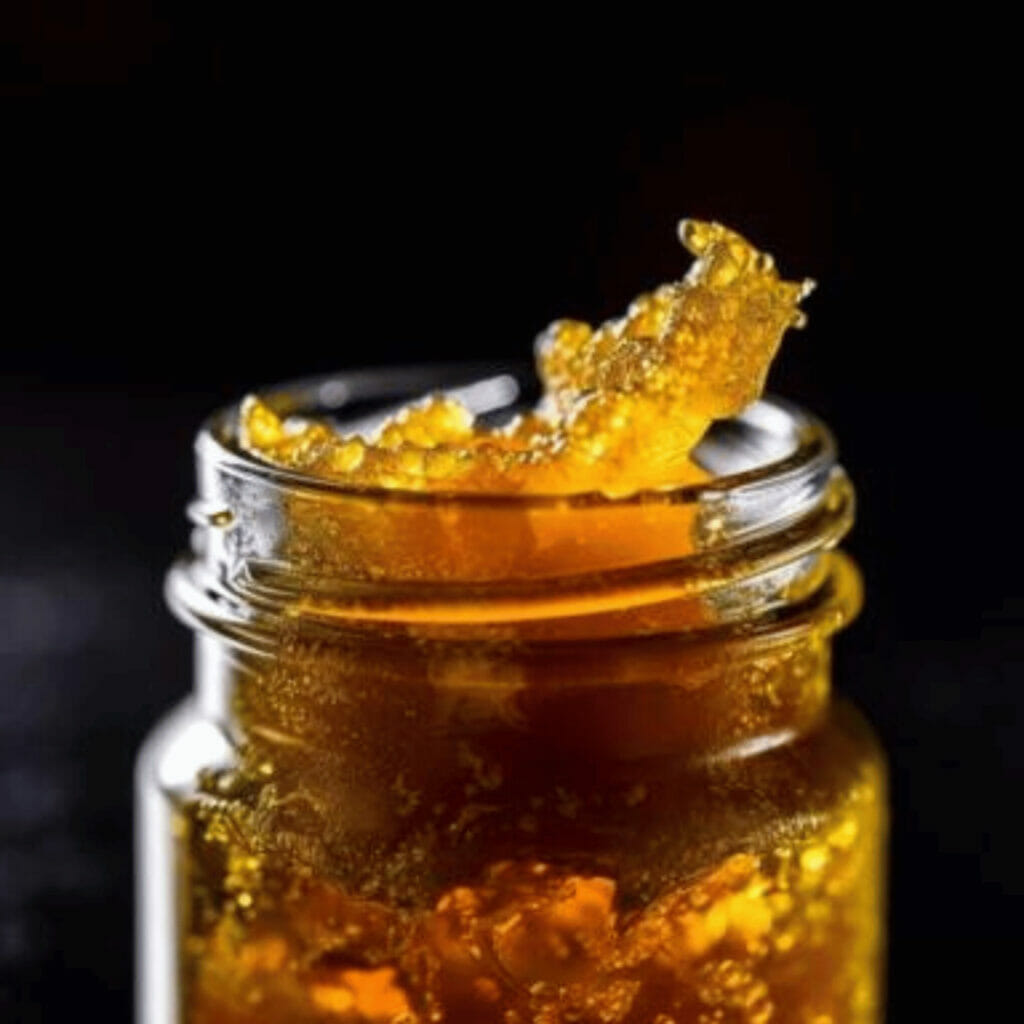
Hash oi1l is a viscous, sticky substance that can vary in appearance from translucent to opaque. The most potent versions can have a THC concentration of approximately 80%.
For comparison, the average THC level in marijuana plants is approximately 12 percent, according to trusted sources. Such high concentrations are achieved through extraction processes, with the most common being the butane hash oil (or BHO) method2.
Production and Characteristics
The extraction process for hash oil involves using a solvent, commonly butane, to isolate THC from the plant’s constituents, resulting in a THC concentration of approximately 80%.
The resultant product may appear translucent or opaque and can be consumed through various methods such as “dabbing” or “burning” using a small blowtorch to heat and vaporize the hash oil. For comparison, traditional marijuana typically has a THC level of approximately 12 percent.
Effects and Potential Risks of Hash Oil
Hash oil can induce euphoria and may help relieve nausea, discomfort, and inflammation. Patients with chronic pain or cancer, for example, might find therapeutic benefits from hash oil. However, like all substances, it carries risks:

- Physical and Psychological Alterations: Users might experience alterations in perception, mood, mobility, and cognitive functions. Some also report memory impairment.
- Adverse Reactions: These can range from fainting and dizziness, paranoia, and anxiety to more severe reactions like hallucinations and even psychosis.
- Cannabis Hyperemesis Syndrome (CHS): This condition is characterized by cyclical episodes of nausea, vomiting, and dehydration and might be linked to chronic use.
- Dependence: Over time, reliance on cannabis can develop, leading to decreased cognitive function and potential withdrawal symptoms when attempting to quit.
Safety and Dependence
While hash oil offers therapeutic benefits, it’s paramount to recognize that there is no safe level of drug use. Individuals might develop a tolerance to cannabis’s effects over prolonged use, leading to increased consumption.
This can spiral into a reliance on cannabis, culminating in withdrawal symptoms during periods of abstinence. These may range from mood disturbances to decreased cognitive function. The method of consumption also plays a pivotal role in the associated risks.
While hash oil can be incorporated into ‘joints’, ‘bongs’, or vaporized, the intensity of its effects can differ based on the method, dosage, and individual tolerance levels.
Consumption Techniques
Hash oil’s consumption has evolved with its growing popularity. Users have devised methods to maximize its effects:
- Dabbing or Burning: This entails using a small blowtorch to generate heat, which then vaporizes the hash oil for inhalation. This method is favored for the rapid and intense effects it delivers.
- Mixing with Traditional Marijuana: Many users opt to enhance their regular smoking experiences by adding hash oil to ‘joints’ or using it in ‘bongs’. Vaporizing has also grown in trend due to the cleaner and more distinct flavor profile it offers.
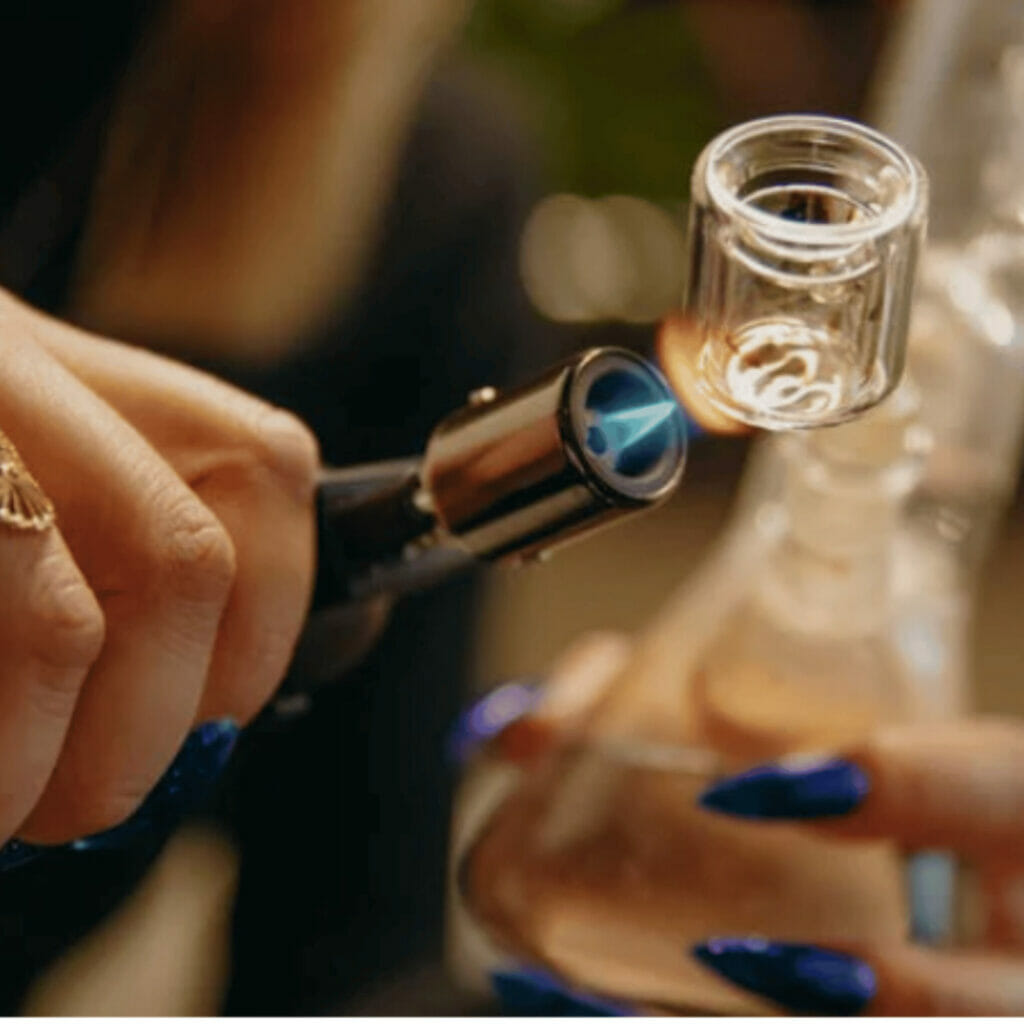

Clinical Benefits and Therapeutic Uses
Hash oil’s potent THC concentration can offer amplified therapeutic benefits:
- Pain Management: Particularly in chronic pain conditions or for cancer patients, the heightened THC levels can provide profound pain relief, more so than traditional marijuana products.
- Nausea and Inflammation: Its anti-inflammatory properties can assist patients with conditions causing chronic inflammation, and its anti-emetic properties can aid those battling chronic nausea.
Potential Adverse Reactions and Safety Concerns
Like all potent substances, hash oil has its set of potential adverse effects:
- Altered States: Elevated THC levels can lead to intense alterations in perception, mood, cognitive functions, and even motor functions. These can sometimes manifest as memory impairment, reduced mobility, or even cognitive impairment.
- Overconsumption Effects: Due to its potency, naive users might experience paranoia, anxiety, hallucinations, or psychosis. There have been documented cases of users experiencing the syndrome of cannabis hyperemesis (CHS), characterized by severe vomiting and nausea.
- Dependence and Tolerance: Chronic users might develop a tolerance, meaning they’d require larger amounts for the same effects. This can lead to a potential reliance on cannabis, making cessation difficult and sometimes leading to withdrawal symptoms.
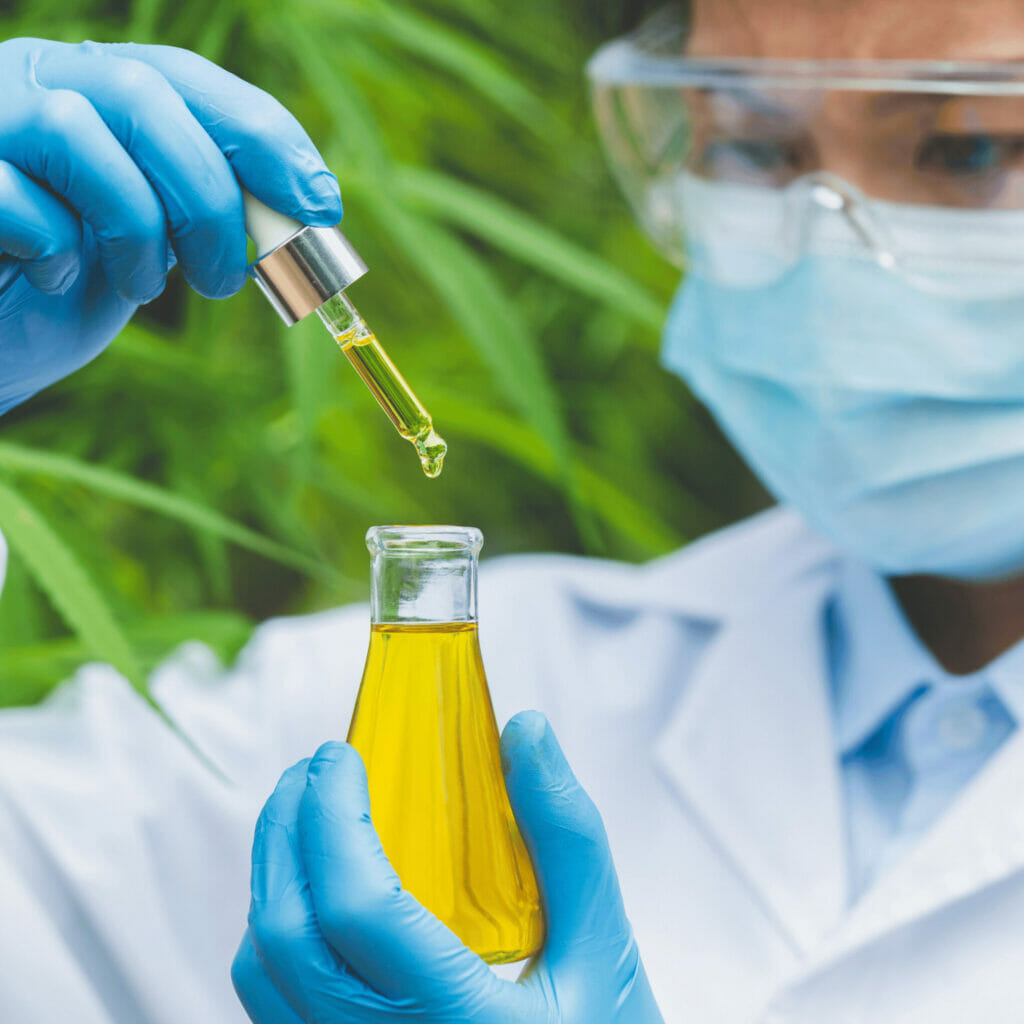

Safety Protocols
- Production
DIY extraction processes3, especially involving butane, can be hazardous. There have been numerous reports of explosions during the extraction process due to the flammable nature of the solvents used. - Driving Under Influence
THC impairs psychomotor skills. Thus, driving under the influence can be extremely hazardous. DUIC (drivers under the influence of cannabis) incidents have been rising in regions where cannabis products are legal. - Long-Term Usage
While occasional usage might have minimal adverse effects, the long-term effects of cannabis, especially in high concentrations like hash oil, remain a topic of ongoing research. Chronic usage has been linked to reduced cognitive functions, potential mental health disorders, and physical health concerns.

Conclusion
Hash oil represents the forefront of cannabis concentrates in both potency and therapeutic potential. Its elevated THC content can offer profound benefits but also brings with it amplified risks. As with all substances, understanding their effects, potential benefits, and hazards can ensure users make informed decisions. Health practitioners should be adequately informed and prepared to guide potential users or those seeking therapeutic benefits from hash oil.
Sources
- Vandergriendt, Carly. “What to Know about Hash Oil.” Healthline, Healthline Media, 30 Oct. 2019, www.healthline.com/health/hash-oil. Accessed 6 Sept. 2023. ↩︎
- “Butane Hash Oil – Alcohol and Drug Foundation.” Adf.org.au, adf.org.au/drug-facts/butane-hash-oil/. Accessed 7 Sept. 2023. ↩︎
- “Residential Marijuana Hash Oil Extraction Information | City of Colorado Springs.” Coloradosprings.gov, coloradosprings.gov/fire-department/page/residential-marijuana-hash-oil-extraction. Accessed 6 Sept. 2023. ↩︎